Few 'Natural Beings' (people) realise how these facts affect us and our everyday lives: Why 'nothing works' and why money comes first - peeps are useful waste products. We must re-claim who and what we really are.
We remain enslaved by the system until we understand how the global corporations work and 're-cognise' our bondage.
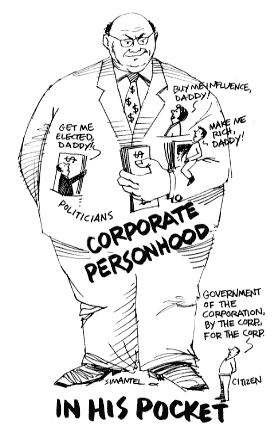
Legal personality (also artificial personality, juridical personality, and juristic personality) is the characteristic of a non-living entity regarded by law to have the status of personhood.
A legal person (Latin: persona ficta) (also artificial person, juridical person, juristic person, and body corporate, also commonly called a vehicle) has a legal name and has rights, protections, privileges, responsibilities, and liabilities under law, just as natural persons (living beings) do. Natural persons are distinct from juridical persons.[1] The concept of a legal person is a fundamental legal fiction. It is pertinent to the philosophy of law, as is essential to laws affecting a corporation (corporations law) (the law of business associations).
Legal personality allows one or more natural persons to act as a single entity (a composite person) for legal purposes. In many jurisdictions, legal personality allows such composite to be considered under law separately from its individual members or shareholders. They may sue and be sued, enter contracts, incur debt, and own property. Entities with legal personality may also be subjected to certain legal obligations, such as the payment of taxes. An entity with legal personality may shield its shareholders from personal liability.
The concept of legal personality is not absolute. "Piercing the corporate veil" refers to looking at individual natural persons acting as agents involved in a corporate action or decision; this may result in a legal decision in which the rights or duties of a corporation are treated as the rights or liabilities of that corporation's shareholders or directors. Generally, legal persons do not have all of the same rights—such as the right to freedom of speech—that natural persons have, although the United States has become an exception in this regard).
The concept of a legal person is now central to Western law in both common-law and civil-law countries, but it is also found in virtually every legal system.[2]
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pin8fbdGV9Y Interestng videos if you can find the time to watch.
Or read on: